The North American Free Trade Agreement: NAFTA's Impact on North American Trade
Explore the impact of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) on North American trade, including its influence on economic growth, trade relations, and market dynamics.

The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) was implemented in 1994 to create a trilateral trade bloc between the United States, Canada, and Mexico. This agreement aimed to reduce trade barriers, promote economic growth and increase cooperation among member countries. Over the years, NAFTA has had a significant impact on North American trade, shaping the region's economy and influencing global trade. The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) members had a total import value of $4.33 trillion in 2023-24. The total exports of the NAFTA countries reached $3.18 trillion as per the global trade data and the North America trade data.
By removing the majority of tariffs and trade barriers and establishing a sizable free-trade zone across the continent, the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) greatly boosted trade between the United States, Canada, and Mexico. This led to a significant increase in cross-border commerce between the three countries, but its effects on specific industries and labor markets are still up for debate. Some contend that it resulted in job losses in certain sectors, especially in the United States as per the US trade data, as businesses moved production to Mexico, where labor costs were much lower. In this article, we will explore the impact of NAFTA on North American trade and how it has shaped the economic landscape of the region.
Important details on how NAFTA affects trade in North America
-
A rise in the volume of trade: Trade between the United States, Canada, and Mexico significantly rose after NAFTA was put into effect as companies benefited from lower tariffs and simpler access to markets.
-
Economic growth: NAFTA is generally regarded as having had a favorable impact on North America's overall economic growth, with increased global trade resulting in higher production and economic trade activity, however, the precise attribution is complicated.
-
Investment flows: Because labor costs in Mexico are lower, NAFTA has made it easier for U.S. businesses to establish operations there.
-
Effect on particular industries: NAFTA had a major impact on some areas, like as manufacturing, where several businesses moved their operations to Mexico to take advantage of lower wages, which may have resulted in the loss of jobs in the United States.
-
Disputes and criticisms: NAFTA was criticized for possible harm to labor standards, environmental issues, and job losses in specific industries, especially in the United States.
Facts to keep in mind regarding the NAFTA
-
The USMCA took the place of NAFTA: The United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), which replaced NAFTA in 2020, sought to resolve some of the problems brought up during the NAFTA era while preserving a free trade area throughout North America.
-
Intricate economic analysis: Other factors, like concurrent global economic trends and technology improvements, make it difficult to pinpoint the exact effects of NAFTA on individual economies.
NAFTA Import Data by Country
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) import data by country showcases the substantial economic exchanges within the region. The United States stands out with a significant import total of $3.17 trillion as per the US import data, highlighting its dominant role in the trade bloc. Mexico follows with imports totaling $598.47 billion, underscoring its substantial economic ties within NAFTA. Canada also plays a vital role in the agreement with imports amounting to $559.23 billion, further emphasizing the interconnectedness of the three countries under NAFTA.
-
USA: $3.17 trillion
-
Mexico: $598.47 billion
-
Canada: $559.23 billion
NAFTA Export Data by Country
The NAFTA export data by country reveals a significant economic impact, with the USA leading the pack at $2.01 trillion, per the US export data, followed by Mexico at $592.99 billion, and Canada at $568.41 billion. These statistics underscore the vital role each country plays in the trade partnership formed under the NAFTA agreement. The figures showcase the substantial trade volume between these nations and emphasize the interconnectedness of their economies within this trade bloc.
-
USA: $2.01 trillion
-
Mexico: $592.99 billion
-
Canada: $568.41 billion
Top 10 Imports by NAFTA Members: Import Data by HS Code
The top 10 imports by NAFTA members based on import data by HS code illustrate the significant trade relationships among the member countries. Analyzing these imports can provide valuable insights into the economic ties and industries driving trade within the NAFTA region. The top 10 import commodities by the NAFTA countries as per the NAFTA trade data for 2023-24 include:
1. Nuclear reactors and machinery (HS code 84): $639.18 billion (14.76%)
2. Electrical machinery and equipment (HS code 85): $637.69 billion (14.73%)
3. Vehicles (HS code 87): $534.41 billion (12.34%)
4. Mineral fuels and oils (HS code 27): $348.09 billion (8.04%)
5. Pharmaceutical products (HS code 30): $204.51 billion (4.72%)
6. Optical, medical, or surgical instruments (HS code 90): $149.87 billion (3.46%)
7. Plastics and articles thereof (HS code 39): $122.37 billion (2.83%)
8. Precious stones and metals, pearls (HS code 71): $110.73 billion (2.56%)
9. Organic chemicals (HS code 29): $85.88 billion (1.98%)
10. Furniture, bedding, and mattresses (HS code 94): $82.97 billion (1.92%)
Top 10 Export Commodities of NAFTA: Export Data by HS Code
The Top 10 Export Commodities of NAFTA, according to the Export Data by HS Code, showcase the significant trade across North America. These commodities play a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscape of the region. From machinery and electrical equipment to vehicles and minerals, each category represents a cornerstone of the international trade market. The top 10 exports by NAFTA members as per shipment data for 2023-24 are:
1. Mineral fuels and oils (HS code 27): $498.87 billion (15.69%)
2. Vehicles (HS code 87): $372.96 billion (11.73%)
3. Nuclear reactors and machinery (HS code 84): $368.98 billion (11.6%)
4. Electrical machinery and equipment (HS code 85): $320.08 billion (10.06%)
5. Optical, medical, or surgical instruments (HS code 90): $140.69 billion (4.42%)
6. Aircraft, spacecraft, and parts thereof (HS code 88): $137.45 billion (4.32%)
7. Precious stones and metals, Pearls (HS code 71): $113.55 billion (3.57%)
8. Plastics and articles thereof (HS code 39): $105.05 billion (3.3%)
9. Pharmaceutical products (HS code 30): $102.25 billion (3.22%)
10. Organic chemicals (HS code 29): $57.93 billion (1.82%)
Search live data by hs code: https://www.usimportdata.com/search-live-data
NAFTA Members Import-Export Trade in the Last 10 Years: Yearly NAFTA Trade Data
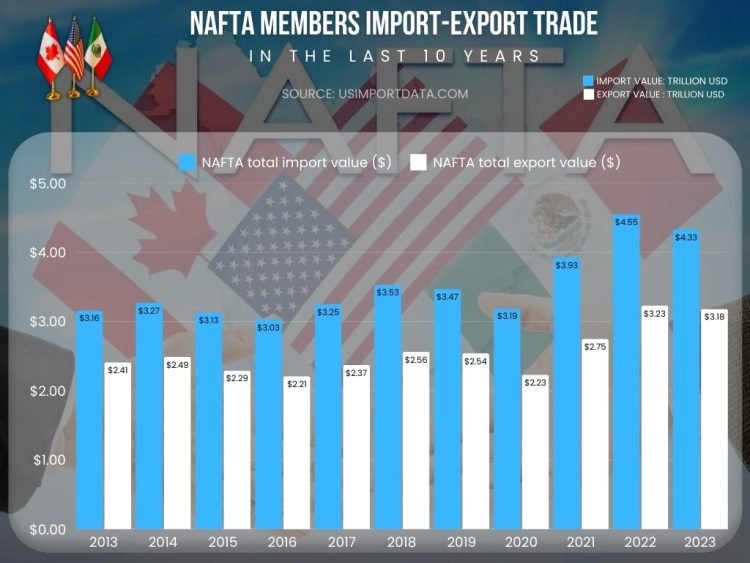
|
Year of Trade |
NAFTA total import value ($) |
NAFTA total export value ($) |
|
2013 |
$3.16 trillion |
$2.41 trillion |
|
2014 |
$3.27 trillion |
$2.49 trillion |
|
2015 |
$3.13 trillion |
$2.29 trillion |
|
2016 |
$3.03 trillion |
$2.21 trillion |
|
2017 |
$3.25 trillion |
$2.37 trillion |
|
2018 |
$3.53 trillion |
$2.56 trillion |
|
2019 |
$3.47 trillion |
$2.54 trillion |
|
2020 |
$3.19 trillion |
$2.23 trillion |
|
2021 |
$3.93 trillion |
$2.75 trillion |
|
2022 |
$4.55 trillion |
$3.23 trillion |
|
2023 |
$4.33 trillion |
$3.18 trillion |
Benefits of NAFTA
One of the key benefits of NAFTA is the removal of tariffs and other trade barriers between member countries. This has facilitated the flow of goods and services across borders, leading to increased trade volumes and economic growth. By eliminating barriers to trade, NAFTA has helped to lower prices for consumers and businesses, making goods more affordable and competitive in the global market.
NAFTA's Influence on Trade Flows
One of the primary goals of NAFTA was to increase trade between the member countries by reducing or eliminating tariffs on goods and services. By creating a free trade zone, NAFTA facilitated a more seamless flow of products across borders, leading to increased exports and imports between the United States, Canada, and Mexico. This resulted in a significant boost to the economies of all three nations, as businesses were able to access larger markets and consumers had greater access to a wider range of products.
Job Creation and Economic Growth
NAFTA has also been credited with creating jobs and stimulating economic growth throughout North America. The agreement opened up new opportunities for businesses to expand their operations and reach new customers, leading to the creation of millions of jobs across various industries. With more trade between the member countries, businesses were able to grow and thrive, contributing to a stronger and more vibrant economy in the region.
Market Integration
NAFTA has also promoted greater market integration among member countries, encouraging cross-border investment and production. Companies are now able to establish operations in multiple countries within the bloc, taking advantage of different resources, labor markets, and consumer bases. This has led to the creation of regional supply chains and increased efficiency in the production process.
Economic Growth
The implementation of NAFTA has had a positive impact on the economies of the United States, Canada, and Mexico. Trade between member countries has grown significantly since the agreement was put into place, leading to increased job opportunities, higher wages, and overall economic development. The agreement has also encouraged foreign direct investment, as companies from around the world look to take advantage of the benefits of trading within the NAFTA Trade Bloc.
Challenges and Criticisms
While NAFTA has brought many benefits to North American trade, it has also faced challenges and criticisms over the years. Critics argue that the agreement has led to the displacement of workers in certain industries, as companies move production to lower-wage countries within the bloc. There are concerns about job losses and wage stagnation, particularly in sectors that have been heavily impacted by increased competition from Mexico.
Renegotiation and USMCA
In response to these criticisms, the United States, Canada, and Mexico renegotiated NAFTA, leading to the creation of the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) in 2018. This updated agreement includes provisions aimed at addressing some of the criticisms of NAFTA, such as improving labor rights, enhancing environmental protections, and modernizing intellectual property rules. The USMCA seeks to build on the successes of NAFTA while addressing the changing dynamics of the North American economy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the North American Free Trade Agreement has had a significant impact on North American trade since its implementation in 1994. By promoting economic growth, market integration, and trade liberalization, NAFTA has helped to shape the region's economy and strengthen ties between member countries. While the agreement has faced challenges and criticisms, the renegotiation of NAFTA into the USMCA demonstrates a commitment to addressing these issues and ensuring that North American trade continues to thrive in the years to come.
Also Read:
Trump's Trade Strategies for US Imports and Exports
What's Your Reaction?




















